Following instructions to guide you on how to install WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment V7 on Linux.
- Installing IBM WebSphere Application Server ND V7
- For installing WAS you can use Launchpad.sh or install script on the WAS Downloaded directory.
- Using Launchpad.
- Using install script.
- Execute ./install to start installation.
- Click on Next
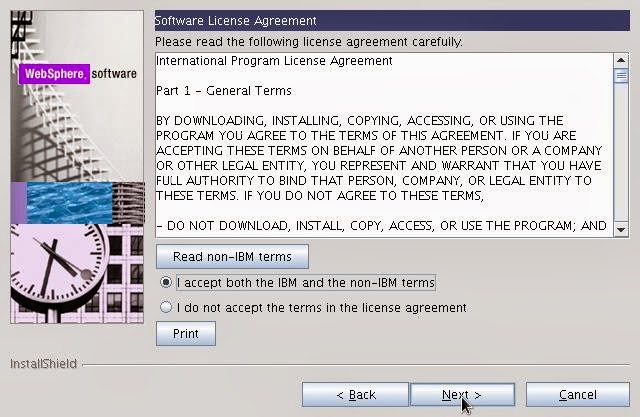
- Select the license agreement and click on Next
- System Prerequisites Check, Ignore the Warning.
- Click on Next.
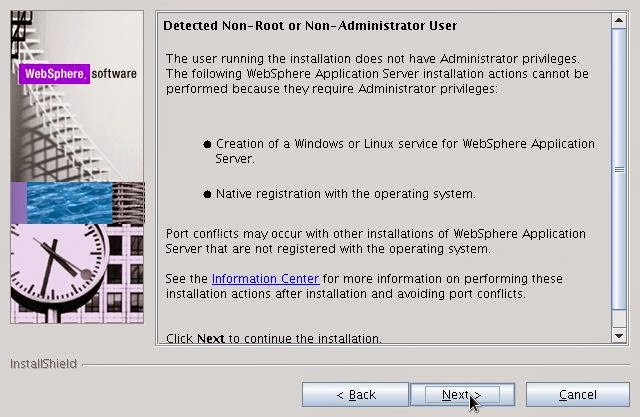
- Checks for User permissions.
- Click on Next.
- Features Selection (Optional).
- Click on Next.
- Select the Installation Manager Directory to be installed. You can leave it default if you wish to install under /opt/IBM
- Click on Next.
- Select the environment for WAS. Here I have selected the default profile, i.e., Cell.
- Click on Next.
- Enable Administrative Security (Optional).
- Click on Next.
- Option for CIM Repository (Optional), as your environment.
- Click on Next.
- Verify permission to perform installation.
- Click on Next.
- Installation Summary.
- Click on Next.
- Installation process started.
- Installation Result. Successfully installed WAS.
- You can check the configuration information viewing “AboutThisProfile.txt” file.
- DMGR Profile Information.
- Check “Launch the First step Console”.
- Click on Finish.
- Check “Installation Verification”.
- That's all! You just installed WebSphere Application Server V7 Network Deployment Successfully.
Now open the Admin Console:
Congratulations, WebSphere Application Server V7 Network Deployment Installed Successfully. I will back soon with more updates soon. If anything wrong in this post Please keep a Suggestion. Thank you. and important thing "Enjoy the Work".


















Comments
Post a Comment